Router Port Forwarding
Port forwarding is a necessary step in setting up a Anyone Relay, allowing external connections to reach your relay's designated port (default: 9001). This universal guide covers the port forwarding process applicable to most routers. It's important to note that while the default port is 9001, you can optionally choose another port.
1. Access Your Router's Settings
In this step we provide examples for different Operating System's on how to get your routers IP-address to access its settings. The IP-address of a router may differ but is typically something like: 192.168.x.x or 10.x.x.x.
If you already know how to access your router's settings then you can skip to next step.
Open Command Prompt
Press Win + R, type cmd, and press Enter to open the Command Prompt.
Run
ipconfig
Type ipconfig and press Enter. Look for the "Default Gateway" entry under the active network connection.
Identify Router IP
Search for and open the 'terminal.app' application.
Copy and paste the below commands in full in the terminal.
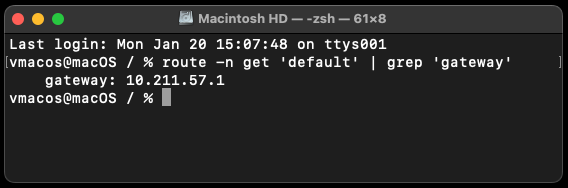
In this example, the output of the commands show that the IP-address of the router is 10.211.57.1. This is the IP-address to open a browser to access router settings.
Search for and open the 'terminal' application.
Copy and paste the below commands in full in the terminal.
In this example, the output of the commands show that the IP-address of the router is 10.211.56.1. This is the IP-address to open a browser to access router settings.
Open Your Web Browser
Now open any web browser and paste the IP-address of the router that you looked up in the previous step.
Login to the Router
Enter your router's username and password. If you haven't changed these, check your router documentation or on the back label, for default credentials.
2. Locate the Port Forwarding Section in your Routers Control Panel
Navigate to Port Forwarding
Look for a section named "Port Forwarding" in your router settings. The location may vary but is often found under the "Advanced" or "Security" tab.
Choose a Device
Select the device running your Anyone Relay from the list of connected devices.
3. Configure Port Forwarding
a. Add a New Rule Create a new port forwarding rule. b. Specify Port Enter the port number Default is normally 9001 otherwise specify your chosen port in the required fields. c. Select Protocol Choose "TCP/UDP" as the protocol. d. Set IP Address Enter the local IP address of your Anyone Relay device. You can find this in your device's network settings. e. Leave source IP empty Do not enter anything in the field for source IP to ensure anyone on the network can connect to your relay on the specified port.
Save your settings, and if required, reboot your network router or firewall.
4. Verify Port Forwarding
Use Online Tools
Utilize online tools like "CanYouSeeMe.org" to check if your specified port is open.
Make sure your Anyone Relay is configured to use the forwarded port. Update the anonrc file with the chosen port accordingly.
5. Security Considerations
Use Strong Passwords
Make sure your router login credentials and Anyone Relay are secured with strong, unique passwords.
Regularly Monitor Activity
Periodically check router logs for any unauthorized access and monitor your relay's performance.
External Resources
For router-specific instructions or troubleshooting, refer to your router's manual or visit the manufacturer's website. Below are links to guides for some popular router brands:
Remember that the steps may vary slightly based on different router models. Always prioritize security and consult your router's documentation for model-specific details. If you can't find your router in the list above, try finding it in this archive: https://portforward.com/router.htm (no need to install any network utilities)