Hardware connectivity
Apps and users connect to the Anyone Network by running the Anon Client.
Most of the Connect section guides you through running the client on your computer, but you can also run it directly from your Anyone Router hardware! Here’s how:
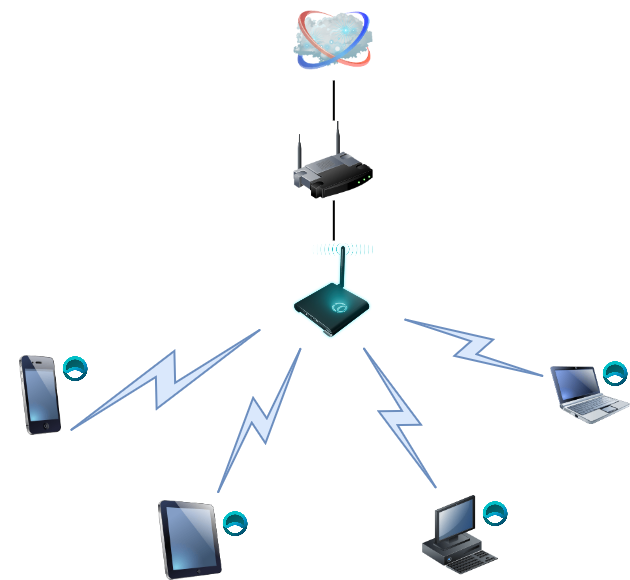
Topology of a typical home router setup
A home router usually sits at the center of the network, connecting to the Internet Service Provider’s (ISP) modem via the WAN (Wide Area Network) port. From there, the router provides connectivity to devices inside the home through two main paths; Wired LAN and Wireless LAN (Wi-Fi).
Anyone Router Feature
The Routing feature allows operators to configure their device to route all hotspot traffic through the Anyone Network. This ensures that clients connecting to the hotspot have their traffic securely routed, enhancing privacy and security.
The Anyone device is placed between your home router (or directly replacing part of its functionality) and your client devices (phones, laptops, IoT, etc.).
Devices in your home connect via Wi-Fi to the Anyone device’s hotspot. The hardware intercepts all the traffic from these clients and forces it through the Anyone network
This feature is implemented using iptables rules to redirect traffic.
DNS traffic (port 53) is redirected to DNSPort 5353 to ensure proper name resolution.
All other traffic is redirected to TransPort 9055, except for DHCP requests.
Example commands used for routing:
These rules ensure that all client traffic is automatically routed through the designated network.
How to Enable or Disable the Routing Feature
Run the wizard once to activate it, see Router Mode Setup or Setup Guide
To toggle the feature, simply turn the hotspot OFF or ON in Network Settings.
Anyone Proxy Beta
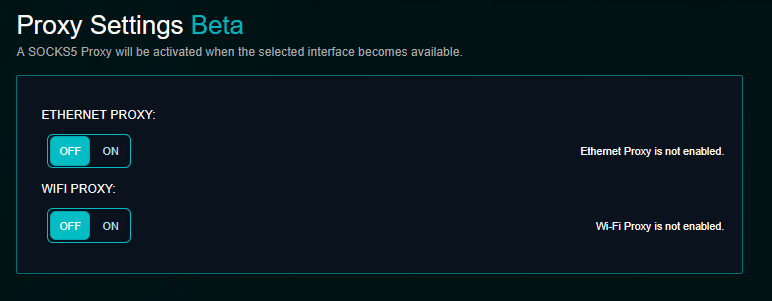
To enable a proxy server on the LAN interface for Ethernet or WiFi, toggle the sliders to enable or disable the proxy on the desired network interface. The interface must be connected for the proxy server to be available for clients to connect.
The Relay will set up a proxy server on port 9050 and apply the necessary policies to restrict connections to clients within the same network.
To learn how to Connect to the Proxy, see the "Connecting to the Network" page for a detailed guide on some common applications.
Last updated